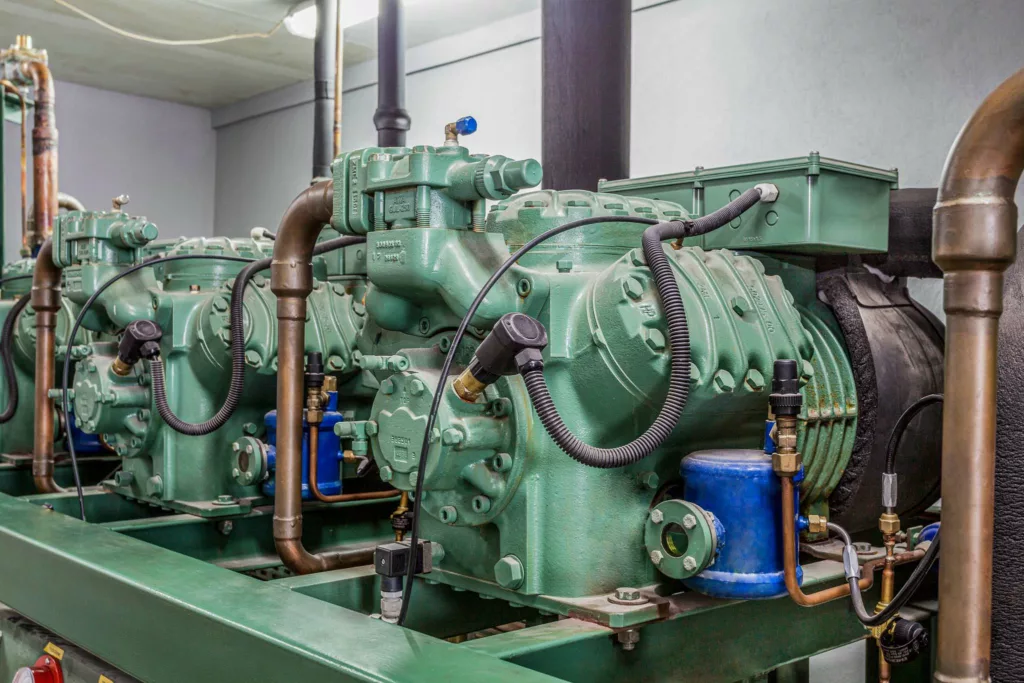
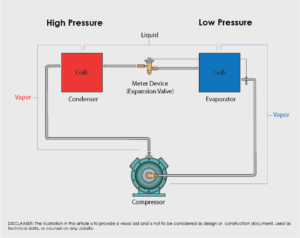
The refrigeration system consists of four main parts, each with a distinctive design intended to perform a task that is closely connected to the refrigeration cycle. NCCER identifies these components as critical devices for the proper functioning of the system.
- Compressor:
In a refrigeration system, the mechanical device converts low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant gas into high, temperature, high-pressure refrigerant gas.The most common type of compressors:
- Reciprocating
- Rotary
- Axial
- Centrifugal
- Condenser:
A heat exchanger device that utilizes coils to transfers heat from the refrigerant flowing inside it to the air or water flowing over it.
- Evaporator:
A device that transfers heat from the air flowing over it to the cooler refrigerant flowing through it by utilizing coils.
- Expansion Valve:
A device that provides a pressure drop that converts high-temperature, high-pressure liquid refrigerant from the condenser into the low-temperature, low-pressure liquid refrigerant entering the evaporator
The most common type of expansion valves:
- Automatic Valves
- Thermostatic Valves
- Capillary Tubes
- Float Valves
To gain a better understanding of how these components function in the refrigeration cycle click on Understanding the Cycle of Refrigeration
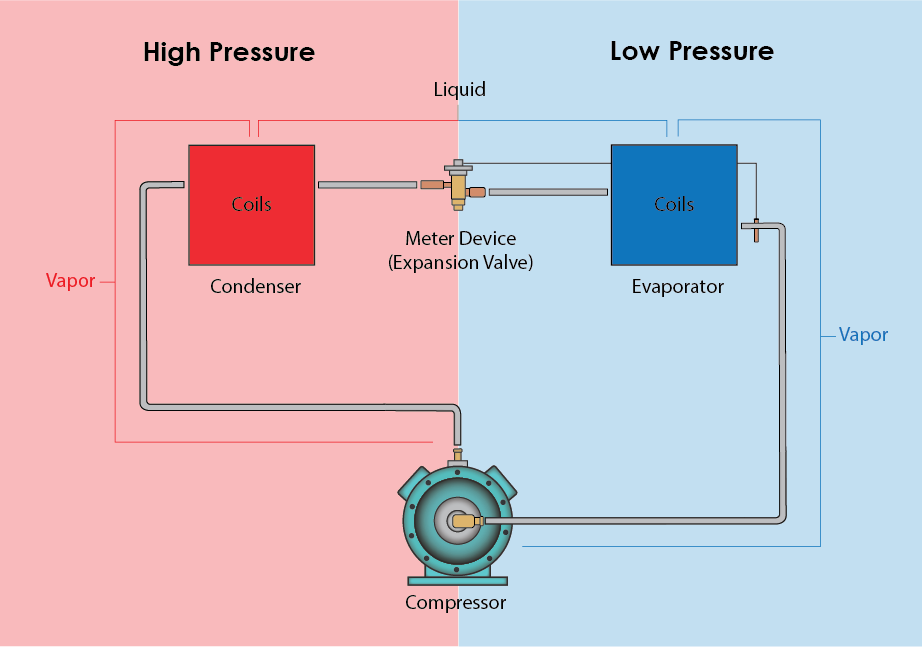
DISCLAIMER: The illustration in this article is to provide a visual aid and is not to be considered as design or construction document, used as technical data, or counsel on any Jobsite.